In today’s fast-paced, digital world, businesses are facing increasing threats to their data security. As a result, traditional network security models have become outdated and insufficient. Enter zero trust – a new approach to cybersecurity that emphasizes the importance of continuous verification, granular access control, and vigilant threat detection. In this article, we’ll explore what zero trust is and why it matters for business cybersecurity.
What is Zero Trust?
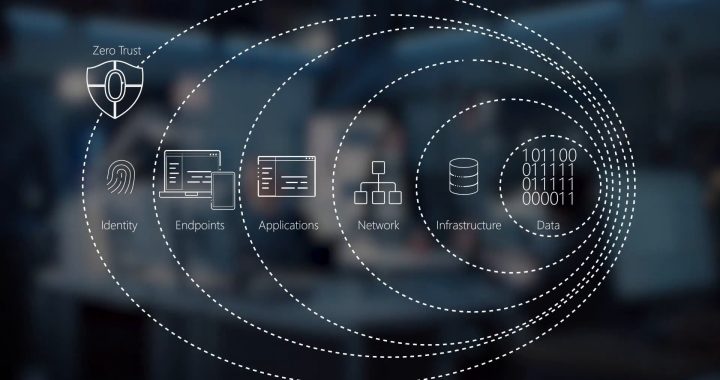
Zero trust is a security concept based on the principle: “Never trust, always verify.” It assumes that all users and devices within an organization are potential threats, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the network perimeter. In this model, access to applications and data is granted on a per-session basis, with continuous verification checks to ensure that users and devices remain authorized.
The Core Components of Zero Trust Architecture Include
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Strong user authentication and authorization processes are critical for ensuring that only verified individuals can access sensitive resources.
- Network Segmentation: Organizations should segment their networks into smaller, more manageable zones to limit the potential impact of a security breach.
- Micro-Segmentation: Within each network zone, granular access controls should be implemented to restrict communication between individual applications and devices.
- Threat Detection and Response: Continuous monitoring and analysis of network traffic are essential for detecting and mitigating security threats in real-time.
Why Does Zero Trust Matter for Business Cybersecurity?
- Enhanced Security Posture: By adopting a zero trust approach, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches by minimizing the attack surface and limiting lateral movement within their networks. This helps to protect against both external threats and insider attacks.
- Improved Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR and HIPAA, require businesses to implement robust security measures. A zero trust architecture can help organizations meet these compliance requirements by providing a more secure environment for handling sensitive data.
- Increased Visibility and Control: Zero trust provides administrators with greater visibility into user activity and device behavior across the entire network infrastructure. This increased control allows them to detect anomalies, respond quickly to incidents, and maintain a strong security posture.
- Greater Flexibility and Scalability: As more businesses adopt cloud-based technologies and remote work arrangements, traditional security models struggle to keep up. Zero trust offers a scalable and flexible solution that can be easily adapted to accommodate changing business needs and emerging threats.
Conclusion
In the face of increasing cybersecurity challenges, it’s clear that relying on outdated security models is no longer sufficient for protecting sensitive data. By embracing a zero-trust approach, businesses can greatly enhance their security posture while also improving compliance, visibility, and flexibility. As more organizations recognize the importance of this innovative cybersecurity strategy, we expect to see continued growth in its adoption across industries worldwide.