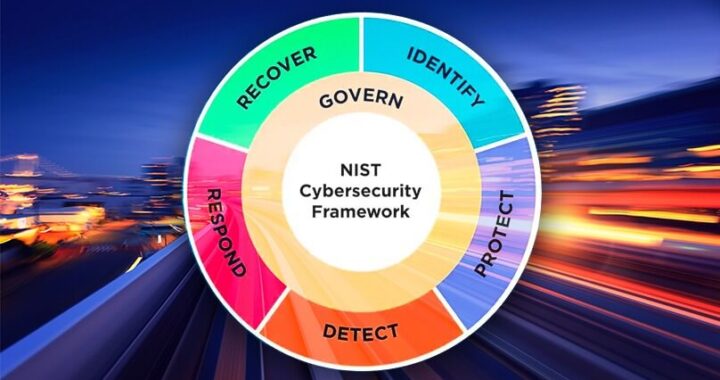
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has recently updated its Cybersecurity Framework for 2024. This is an important development that businesses need to take into account when developing their own cybersecurity best practices. In this article, we will discuss the changes made by NIST and how businesses can use these updates as a reference point for their own cybersecurity frameworks.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) was first released in 2014 as a voluntary set of guidelines for organizations to help manage and reduce cybersecurity risks. The 2024 update is intended to address the rapidly evolving threat landscape and provide businesses with more robust tools for protecting their digital assets. Some of the key changes made by NIST include:
- Enhanced focus on risk management: The new framework places a greater emphasis on identifying, assessing, and managing risks in a proactive manner. This includes regularly monitoring and evaluating cybersecurity measures to ensure they remain effective against emerging threats.
- Greater emphasis on supply chain security: The updated framework recognizes the importance of securing third-party vendors and partners as part of an organization’s overall cybersecurity strategy. Businesses need to pay careful attention to the security practices of their suppliers and work with them to mitigate risks.
- Integration of emerging technologies: The new framework includes guidance on how businesses can leverage emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to improve their cybersecurity posture. This involves using these tools to identify patterns, predict threats, and automate responses to potential security incidents.
- Improved alignment with international standards: NIST has updated the framework to better align with global cybersecurity standards, including those set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). This allows businesses to more easily compare their cybersecurity practices with those of organizations in other countries.
To effectively use the NIST Cybersecurity Framework as a reference point for their own best practices, businesses should consider the following steps:
- Conduct a risk assessment: The first step is to identify and assess your organization’s cybersecurity risks. This involves evaluating the potential impacts of various threats on your digital assets and prioritizing those that pose the greatest danger.
- Develop a risk management plan: Based on your risk assessment, develop a comprehensive plan for managing and mitigating cybersecurity risks. This should include policies, procedures, and controls designed to protect against identified threats and vulnerabilities.
- Implement security measures: Put in place the necessary technical and administrative controls to protect your digital assets from potential attacks. This may involve installing firewalls, encrypting sensitive data, and training employees on cybersecurity best practices.
- Monitor and review your cybersecurity posture: Regularly review and update your risk management plan to ensure it remains effective in the face of evolving threats. This may involve adjusting security measures, updating employee training materials, or working with third-party vendors to improve their security practices.
- Communicate with stakeholders: Finally, make sure that all relevant stakeholders are aware of your organization’s cybersecurity policies and procedures. This includes employees, suppliers, partners, and customers, as well as regulatory bodies and industry groups.
In conclusion, the NIST Cybersecurity Framework is an important resource for businesses looking to improve their cybersecurity practices. By understanding the changes made in the 2024 update and implementing the recommended best practices, organizations can better protect themselves from emerging threats and maintain a strong security posture.