Network security has become a top priority for businesses and organizations of all sizes, and rightfully so. Improperly configured or secured networks can create a playground for malicious hackers and automated attacks.
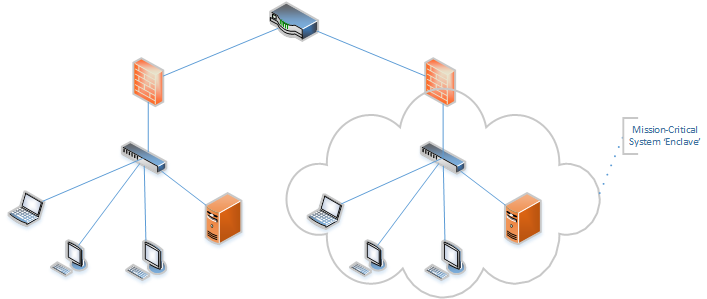
One critical aspect of maintaining robust cybersecurity is segmenting networks to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Network segmentation involves dividing a single network into multiple smaller sub-networks or segments, each with its own set of rules and restrictions. This approach not only improves overall security but also enhances productivity, reduces downtime, and minimizes the attack surface.
Why Segment Networks?
Segmenting networks is essential for several reasons:
- Prevents Lateral Movement : By isolating sensitive devices on separate networks, an attacker who gains access to one segment cannot easily move laterally to other areas of the network.
- Limits Damage in Case of a Breach : If a device on a segmented network is compromised, the damage is contained within that specific segment, preventing it from spreading to other parts of the network.
- Reduces Attack Surface : Segmenting networks reduces the number of potential entry points for attackers, making it more difficult for them to gain access.
Segmenting Untrusted Devices
Untrusted devices, such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices, phones, cameras, and guests’ computers, should be kept on separate networks than business computers, servers, and other sensitive devices. This is because these devices are often unpatched, outdated, or vulnerable to exploitation. Larger organizations may also segment networks by groups or teams, such as separating the sales and financial team as they likely access differentiated resources.
Segmenting Wireless and Wired Networks
Segmenting wireless and wired networks is also crucial for maintaining robust cybersecurity:
- Wireless Networks : Wireless networks should be segmented from wired networks to prevent unauthorized access via Wi-Fi.
- Wired Networks : Sensitive devices, such as servers and databases, should be kept on wired networks rather than wireless ones, which are more vulnerable to hacking.
Benefits of Segmented Networks
Segmented networks offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Security : Segmenting networks reduces the attack surface and limits damage in case of a breach.
- Enhanced Productivity : By isolating sensitive devices, you can prevent unauthorized access and ensure that only authorized personnel have access to specific resources.
- Reduced Downtime : Segmented networks reduce the risk of downtime caused by security breaches or malware outbreaks.
Best Practices for Network Segmentation
To implement effective network segmentation:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment : Identify sensitive devices and data that require isolation.
- Implement Firewalls and Access Control Lists (ACLs) : Use firewalls and ACLs to restrict access between segments.
- Use Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) : VLANs allow you to segment networks without physical changes.
- Monitor Network Traffic : Regularly monitor network traffic to detect potential security threats.
Final Thoughts
Network segmentation is a critical aspect of maintaining robust cybersecurity. By segmenting untrusted devices, wireless and wired networks, and implementing best practices, organizations can improve their overall security posture, reduce downtime, and minimize the attack surface.
If your organization needs a hand with cybersecurity, reach out. We’re happy to help.